Starting from the source, the whole process of product processing is strictly in accordance with ISO9001, HACCP and SC, and electronic monitoring, on-site inspection of quality inspection and other means are used throughout the process, and it is filed for investigation. Before leaving the factory, the product must pass the self-inspection, random inspection and inspection, etc., and can only leave the factory with a qualified inspection report. Strengthen the staff's quality awareness and standard operation training, and all production personnel will be put into operation after passing the examination. The operation regulations are in accordance with the requirements of ISO9001, HACCP and SC production. The inspectors have relevant operation skills and compliance qualifications. Strict quality inspection and quality traceability are carried out in all aspects of raw material procurement, processing procedures, environmental hygiene, packaging materials, storage and transportation.
Ⅰ、 Material section management:
1. Screening and audit process of material suppliers.
2. Sampling, acceptance and distribution of materials: ①Sampling: formulate sampling plans and operating procedures, with representative sampling; ②acceptance: judgment and QC inspection of raw and auxiliary materials identification, appearance characteristics, etc .; daily acceptance and QC inspection of packaging materials; ③ inspection : Conventional physical and chemical index tests: acid value, peroxide value, saponification value, pH value, TLC identification, relative density, refractive index, loss on drying, ash, ignition residue, etc .; microbial limit check: total bacteria, mold, yeast Bacteria, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, Hemolytic streptococcus; Heavy metals: lead, arsenic, mercury, etc .; Determination of functional ingredients: high performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, atomic fluorescence spectrometry , Atomic absorption spectrophotometry, ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry, titration. ④Issuance: Qualified inspection, QA issuance, unqualified inspection, implementation of unqualified material management process.
3. The processing flow of unqualified materials.
4. Review of label samples to establish standard proofs of labels: ① review of label design drafts; ② review of the first printed version of labels, establish standard proofs; ③ entrust processing products, customers provide standard proofs of product labels; ④ acceptance content: text, Patterns, colors, cutting quality, folding direction of machine-labeled stickers, effects of stickers, etc.
5. Standardize the material name and determine the material code: ①Original and auxiliary materials: name + specification + supplier (manufacturer), indicating the expiration date; ②Internal packaging materials: category + material + specifications + color + supplier; ③ outer packaging materials: label , Instruction manual, small box, middle box, carton and aluminum foil: name + trademark + specification + version number + supplier board, partition, sealing film, plastic: name + specification + supplier.
6. Inspection before product delivery ①Customer name; ②Product name specification; ③Quantity; ④Inner and outer packaging; ⑤Marking.
7. Sample retention management: ① Sample retention room management The sample retention room is an independent, lockable room and is managed by a dedicated person. The samples are placed under the storage conditions that meet the requirements, marked, and the samples with temperature and humidity records should be registered in time, and the storage must be approved and recorded in detail; ②The samples of the sample retention project should be subject to the stability test management regulations Check the normal condition of ordinary samples, conduct appearance inspection every three months, and conduct full inspection according to the standard every other year; ③Storage period materials: according to the provisions of the material storage period, but not less than 1 year finished products: +1 after the expiration date year.
8. In-store quality inspection: ①In-store quality inspection of materials and finished products, and handle any problems found in time. ② Management in the near term. ③ The material is executed "first in first out", and the finished product is "first produced first and sold first". ④Inspect the inventory products before delivery, and put forward handling suggestions.
Ⅱ、 Production site management:
1. Production process monitoring: a. The appearance and quality of raw and auxiliary materials before feeding are qualified; b. The raw and auxiliary materials are weighed accurately when feeding; c. The intermediate products after mixing meet the process requirements; d. Inspection according to the inspection items of product standards. c. The quantity of the inner packaging is accurate, and the error is within the allowable range; d. The inner packaging bottle / bag should be tightly sealed; e. The batch number, production date, and expiration date printed on the outer packaging are correct, clear, and there is no missing print; f. Firm; g. Packing and packing contents and quantity are accurate and correct.
2. Routine physical and chemical index inspection: acid value, peroxide value, ash, moisture, non-volatile matter, residual solvent, total flavonoids, disintegration time limit, etc.
3. Heavy metals: lead, arsenic, mercury, calcium, iron, zinc, cadmium, copper, etc.
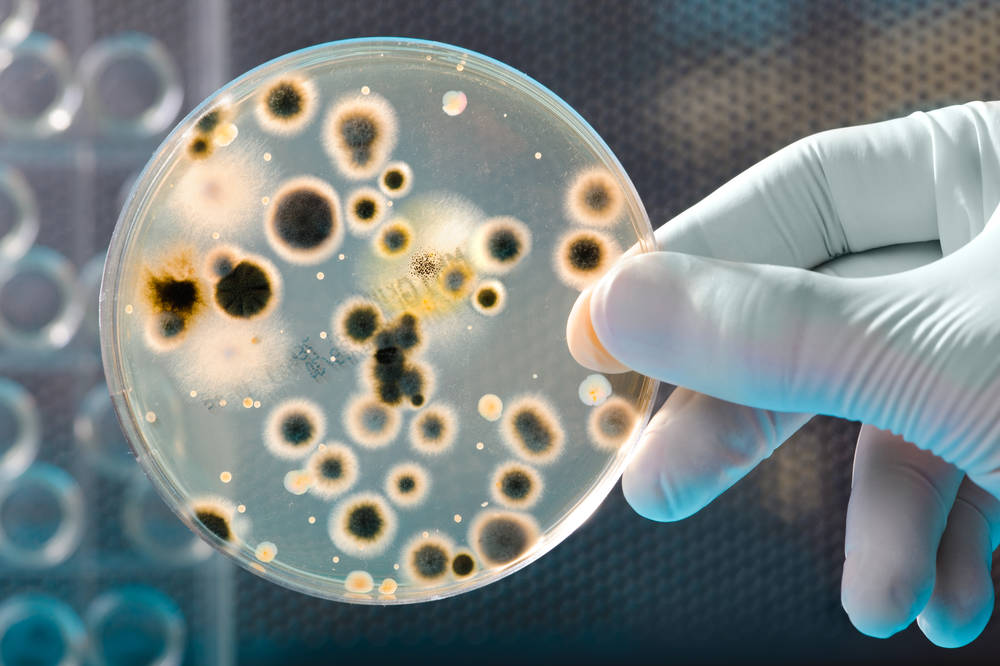
4. Microbial limit check: total bacteria, mold, yeast, coliform bacteria, salmonella, shigella, staphylococcus aureus, hemolytic streptococcus.
5. Determination of content: high performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, atomic fluorescence spectrometry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry, ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry, titration.
6. Check according to product standards.
Clean area environment control: Determine whether the environment meets the expected setting by sampling and testing the air, walls, ceiling, equipment surface and people in the clean area. (①Microbial count monitoring: sedimentation bacteria method; ②Dust particle count monitoring: dust particle counter method; ③Personal hygiene monitoring: contact dish method or cotton ball wiping method; ④Surface microorganism monitoring: cotton ball wiping method , Ceiling, equipment surface, etc.).
Establish a key control point in the workshop: carry out daily follow-up inspections on the implementation of the production process, improve operator awareness, and improve the production environment; measurement instrument management: ① track the use of measurement instruments: whether the operators use the measurement instruments correctly and whether the measurement instruments are in a normal state; ② Regularly calibrate the measuring instruments, generally the QA calibrates every two weeks; ③ The measuring instruments are periodically verified and have a green qualified mark, and indicate the calibration period and calibration unit.
Production process quality analysis: ① irregularly organize relevant departments to analyze the causes of quality problems that have occurred in the production process, and take corresponding corrective measures to track the implementation. ②Summarize and analyze the quality accidents in the production process every month to reduce the incidence of process accidents. ③When the customer complains about quality problems, cooperate with the work of QA regulations, put forward suggestions for improvement, and actively track the implementation status of the improvement.
Release of finished products: Each batch of finished products must pass the QA inspection and be issued with a product qualification certificate before being put into storage. ①The whole production process-in line with regulations ②Batch production records-complete and accurate ③Products-qualified
Ⅲ、 Regulatory support:
Product after-sales service;
Master the national policy and regulatory documents, implement and implement them;
Standardization work: ①Establish and perfect enterprise standards for own products, ②Assist customers to establish product enterprise standards, ③Enterprise standard filing.
License application, review and replacement, production license ;
Implementation and certification of industry standards: ① Hygiene registration certificate for export products, ② Certificate of conformity of measurement assurance system, ③ File management.
Training: ① training for new employees, ② operation specification training, ③ quality management training, ④ production process training, ⑤ hygiene knowledge training, ⑥ operation process training, ⑦ fire safety training, ⑧ environmental protection knowledge training, ⑨ HACCP training, ⑩ ISO9001 training, ⑪ ISO14000 Training, ⑫ team development training.
Ⅳ、 Laboratory management:
Inspection personnel: 100% of the inspection personnel are undergraduates and above, and all personnel have passed the national employment certificate.
Quality standards: In addition to the implementation of the national legal standards for health foods, all products and materials have established enterprise internal control quality standards that are higher than the legal standards.
Product stability inspection: Establish a product stability inspection system based on the "Guidelines for the Stability Test of Health Foods" and conduct regular monitoring of products during the storage period to ensure that the product quality meets the requirements during the period.
Type inspection: regularly send the product to the National Processed Food and Food Additive Quality Supervision and Inspection Center (Nanjing) and Jiangsu Product Quality Supervision and Inspection Research Institute for third-party inspection to ensure the accuracy of the inspection data.










 沪ICP备11012790号-6
沪ICP备11012790号-6 营业执照
营业执照 沪公网安备31010702005226号
沪公网安备31010702005226号